

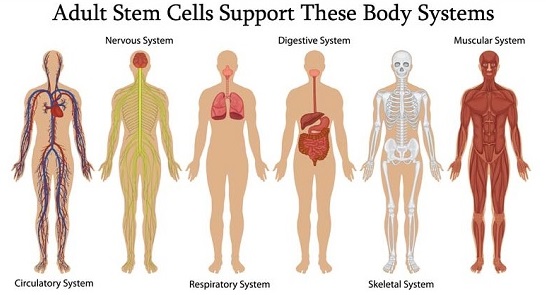
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can turn into specific cells, as the body needs them. No other cell in the body other than stems cells has the natural ability to generate new cell types.Ĭells in the body have specific purposes, but stem cells are cells that do not yet have a specific role and can become almost any cell that is required. These daughter cells become either new stem cells or specialized cells with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. Stem cells are the body’s raw materials, cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Stem cells offer great promise for new medical treatments. Researchers believe that stem cell-based therapies may one day be used to treat serious illnesses such as paralysis and Alzheimer disease. In some cases, they can also fix damaged tissues. This can range from muscle cells to brain cells. After years of research scientists seem to be on the brink of success with a number of stem cell treatments which could change medicine forever.Stem cells are special human cells that are able to develop into many different cell types. Scientists have been using them for years in bone marrow transplants, and they are now investigating different types of adult stem cells, and how they might control the way they develop. It's ethically tricky too, because the stem cells come from human embryos.Īdult stem cells offer another possible route. The clinical challenge is to encourage the embryonic stem cells to develop into the type of cells we need, without them growing into we don't want. Scientists have found ways to grow embryonic stem cells in the lab, and are trying to use them to cure conditions such as diabetes (by replacing the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas), or enable people paralysed by spinal injuries to walk again by re-growing spinal nerves. Using human stem cells in medicine is quite another. That's massively useful for lots of things, like producing orchids and other house plants quickly and cheaply, conserving endangered species, or making clones of plants that have been genetically modified to deal with environmental stresses. Plant stem cells can be used to make clones, identical copies of the parent plant. Each one has the potential to form a whole new plant! Unsurprisingly, people want to make use of these amazing cells. The big difference is that the stem cells in adult plants can still make every type of plant cell. They're found at the meristems, the growing tips of the roots and the shoots. For example bone marrow stem cells only form different types of blood cells. But the adult stem cells are more limited in the types of cell they can make. They also start to differentiate, to become specialised for different purposes.įor example, red blood cells look very different from nerve cells, but they both start out as embryonic stem cells.Īdults don't have any embryonic stem cells, but they do still have stem cells - they're essential for replacing or repairing normal cells which become damaged, or worn out. The stem cells continue to divide by mitosis, and so the embryo grows. The cells on the inside layer of this very early embryo can make all of the cell types needed in your body. This then divides by mitosis to form two identical cells, and they just keep on dividing to form a hollow ball of 200-300 tiny cells. We're all very complex organisms, made up of lots of different types of cells carrying out different jobs in our bodies such as nerve cells, blood cells, fat cells and muscle cells.Įach one of us starts off as a single cell when an egg and a sperm join together.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
